By Alexander Hasse
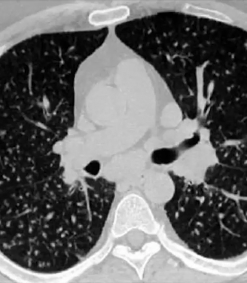
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) is a relatively rare but underdiagnosed disease characterized by repeated infiltration of thrombotic material into the pulmonary artery vessels. Left untreated, the disease has a poor prognosis due to progressive right heart failure. However, CTEPH is the only potentially curatively treatable disease from the group of pulmonary hypertension. Operable patients can be cured by means of pulmonary endarterectomy. For the inoperable third of patients, pulmonary balloon angioplasty (BPA) is a radiological interventional procedure. In order to measure the therapeutic success of this intervention and to be able to make any prognostic statements, In addition to clinical evaluation, the right heart catheter is still indispensable as the gold standard. However, as an invasive procedure, it carries the risk of serious complications. Cardiac magnetic resonance tomography is suitable as a non-invasive and therefore safer and quicker procedure. This study uses volumetrics, strain analysis and cardiac mapping to first examine whether BPA has a positive effect on (right) heart function and pulmonary hemodynamics. Furthermore, correlations between pulmonary hemodynamics and strain parameters as well as T1 and T2 times are checked and it is determined to what extent right ventricular strain analysis is suitable for monitoring the effects of therapy. Cardiac magnetic resonance tomography is suitable as a non-invasive and therefore safer and quicker procedure. This study uses volumetrics, strain analysis and cardiac mapping to first examine whether BPA has a positive effect on (right) heart function and pulmonary hemodynamics. Furthermore, correlations between pulmonary hemodynamics and strain parameters as well as T1 and T2 times are checked and it is determined to what extent right ventricular strain analysis is suitable for monitoring the effects of therapy. Cardiac magnetic resonance tomography is suitable as a non-invasive and therefore safer and quicker procedure. This study uses volumetrics, strain analysis and cardiac mapping to first examine whether BPA has a positive effect on (right) heart function and pulmonary hemodynamics. Furthermore, correlations between pulmonary hemodynamics and strain parameters as well as T1 and T2 times are checked and it is determined to what extent right ventricular strain analysis is suitable for monitoring the effects of therapy.
Product Details
- Publisher: Springer; 1. Aufl. 2021 edition (July 6, 2021)
- Language : German
- Paperback : 71 pages
- ISBN-10 : 3658345411
- ISBN-13 : 978-3658345419
- ISBN-13 : 9783658345419
- eText ISBN: 9783658345426